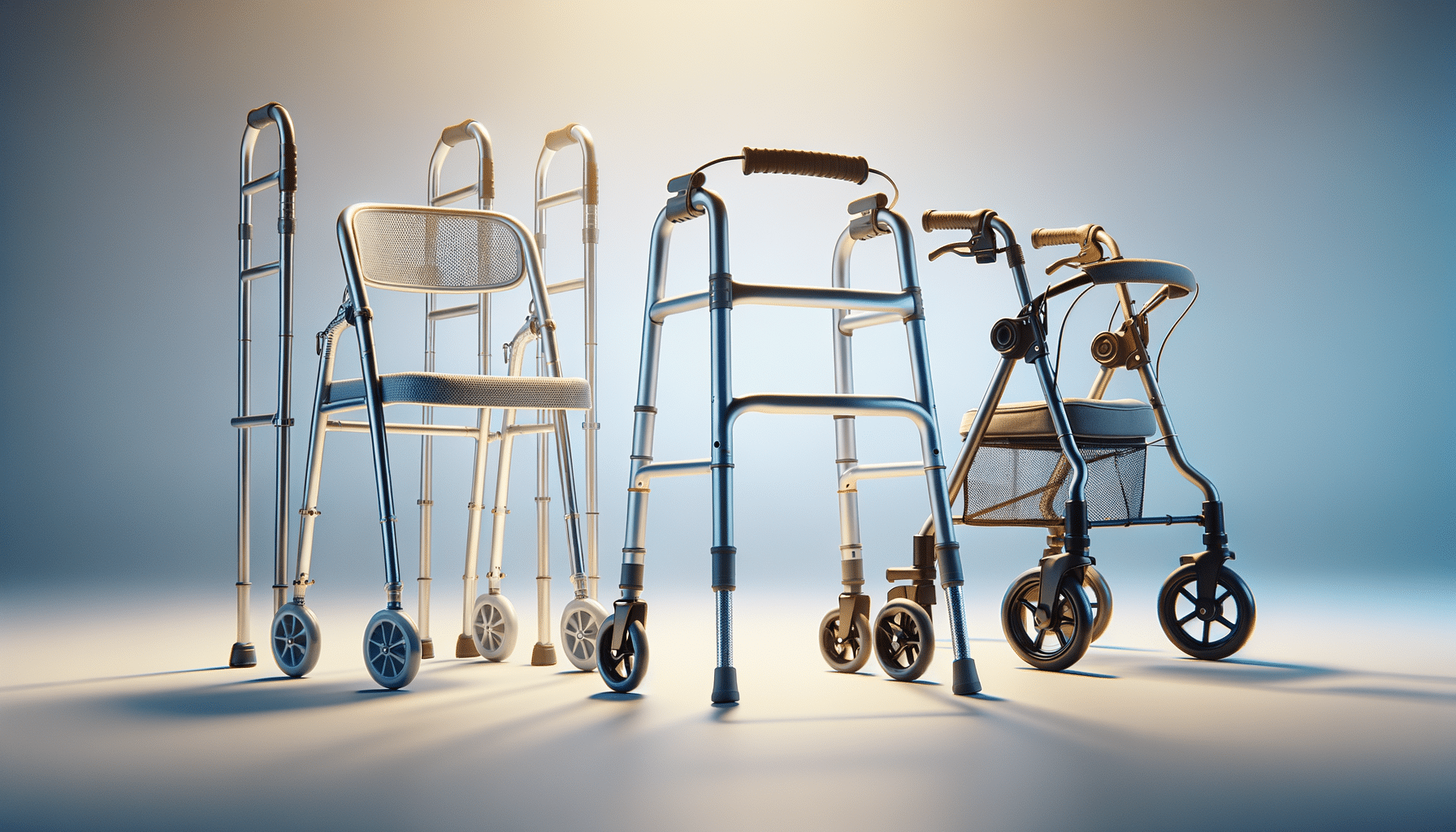
Compare Walker Types: Standard, Two-Wheel, and Rollator
Introduction to Walkers for Seniors
As we age, maintaining mobility becomes increasingly important for independence and quality of life. Walkers are essential tools for many seniors, providing support and stability to those who need assistance with walking. However, not all walkers are created equal, and choosing the right one can make a significant difference in comfort and usability. This article compares three popular types of walkers: standard, two-wheel, and rollator, helping you make an informed decision based on individual needs.
Standard Walkers: The Basics
Standard walkers are among the most straightforward mobility aids available. They consist of a simple frame with four legs, all equipped with rubber tips to prevent slipping. These walkers require the user to lift and move the device forward, which can be beneficial for those who need maximum support and stability.
Pros of standard walkers include:
- High stability due to the four-legged design.
- Lightweight and easy to maneuver in tight spaces.
- No moving parts, which reduces the risk of mechanical failure.
However, standard walkers may not be suitable for everyone. They require a fair amount of upper body strength and coordination to lift and move, which can be challenging for some seniors. Additionally, they may not be ideal for those who need to cover longer distances or who have limited strength in their arms and hands.
Two-Wheel Walkers: A Step Forward
Two-wheel walkers offer a middle ground between standard walkers and rollators. They feature two wheels on the front legs, allowing the user to push the walker instead of lifting it. This design can be particularly beneficial for seniors who find lifting a standard walker challenging but still require substantial support.
The advantages of two-wheel walkers include:
- Reduced effort needed to move the walker forward.
- Increased ease of use on various surfaces.
- Maintained stability, as the back legs remain stationary.
Despite these benefits, two-wheel walkers may not provide the same level of support as standard walkers, especially on uneven surfaces. They are best suited for individuals who can balance well but need assistance with fatigue or minor stability issues.
Rollators: Enhanced Mobility
Rollators, or rolling walkers, are equipped with four wheels and often come with additional features such as seats and storage baskets. They are designed for those who need a mobility aid that offers both support and convenience over longer distances.
Key benefits of rollators include:
- Ease of movement, thanks to the four-wheel design.
- Built-in seating for resting during walks.
- Added storage options for personal items.
However, rollators are generally heavier than other types of walkers and may require more strength to control. They are most suitable for seniors who have good balance and can handle a slightly more complex device. The additional features also mean they tend to be more expensive, which is an important consideration for many users.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Walker
Choosing the right walker involves considering personal mobility needs, physical strength, and the environments in which the walker will be used. Standard walkers offer maximum stability but require more effort to use. Two-wheel walkers provide a balance of support and ease of movement, while rollators offer enhanced mobility and convenience for those who can manage them.
Ultimately, the decision should be guided by the user’s specific needs and preferences. Consulting with healthcare professionals can also provide valuable insights and recommendations tailored to individual circumstances. By understanding the differences between walker types, seniors and their caregivers can make informed choices that enhance mobility and independence.